The Electoral Bond Scheme in India, introduced through amendments to various Acts, was intended to revolutionize political funding by offering an anonymous donation mechanism. However, the scheme has faced intense criticism for its lack of transparency and potential for misuse. The bonds, available in various denominations, allow individuals and companies to make donations to political parties without disclosing their identities, raising serious concerns about accountability and the influence of money in politics. Critics argue that the scheme undermines democracy by enabling untraceable donations, potentially leading to quid pro quo deals, favoritism, and corruption. The lack of spending restrictions on these funds has raised fears that they could be used for purposes other than elections, diluting the intended purpose of clean political funding. Additionally, the Supreme Court’s recent ruling declaring the scheme unconstitutional underscores the fundamental flaws in its design and implementation.
The revelation that a significant portion of electoral bond purchases came from loss-making entities, shell companies, and foreign firms further highlights the loopholes in the system that allow for the circumvention of donation limits and concealment of donors’ identities. The scheme’s impact on the democratic process is evident in the disproportionate funding received by certain political parties, raising questions about fairness and the level playing field for all parties. The delayed scrutiny and disposal of challenges to the scheme have also drawn criticism, emphasizing the need for timely and decisive action to uphold the integrity of the electoral process. The role of investigative agencies in relation to the timing of bond purchases has sparked concerns about potential misuse of power for political gain, further eroding public trust in the system.
In conclusion, the Electoral Bond Scheme, despite its noble intentions of promoting clean political funding, has fallen short of its objectives. The lack of transparency, accountability, and safeguards against misuse have compromised the integrity of the electoral process and raised serious questions about the influence of money in politics. Moving forward, there is a pressing need for comprehensive reforms to ensure transparency, fairness, and accountability in political funding to safeguard the principles of democracy.
What is the purpose of electoral bonds

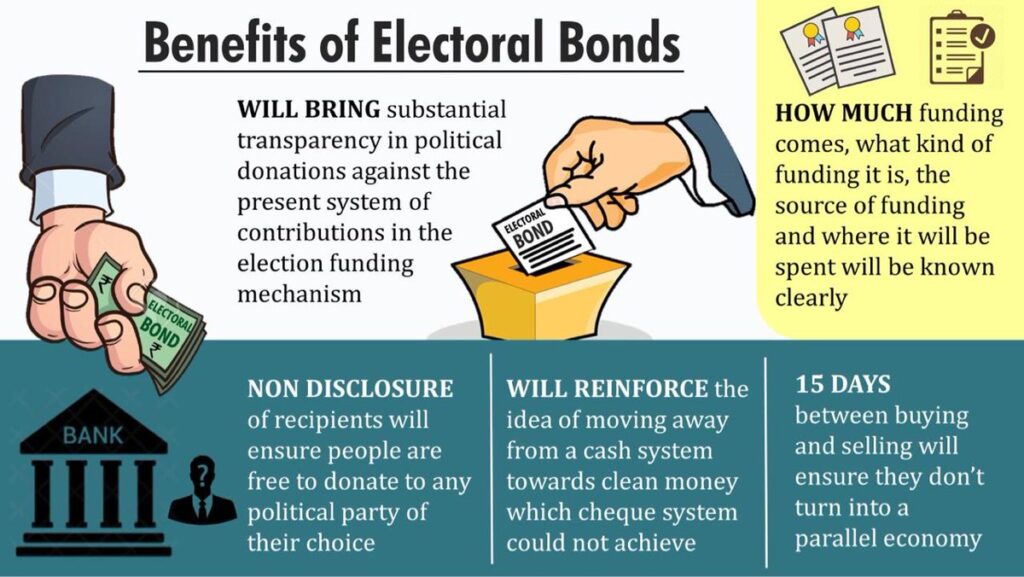
The purpose of electoral bonds is to facilitate transparent funding of political parties while maintaining the anonymity of donors. Introduced in India in 2017, these bonds are interest-free bearer bonds or money instruments that can be purchased by companies and individuals to donate to political parties. The bonds can be purchased from designated branches of authorized banks, and the donor can remain anonymous while making the donation. The political parties have to encash them within a stipulated time, and the funds received through electoral bonds are credited to the party’s designated bank account, which is monitored by the Election Commission of India (ECI).
The objective of electoral bonds is to enhance transparency in political funding by routing donations through bonds, recording transactions by the issuing banks, and monitoring them by regulatory authorities. They also provide a legal framework for making political donations, thereby reducing the reliance on cash contributions, which are often associated with opacity and potential misuse. Additionally, electoral bonds encourage donations through formal banking channels, promoting transparency and accountability in financial transactions related to political funding.
However, electoral bonds have also faced criticism and scrutiny from various quarters. Critics argue that the anonymity of donors undermines transparency and accountability in political funding, as it allows for potential influence peddling without public scrutiny. The lack of disclosure of the identities of individual donors has raised concerns about the potential for quid pro quo arrangements between donors and political parties. Despite the legal framework governing electoral bonds, there are concerns about the possibility of misuse or circumvention of regulations, particularly in the absence of stringent enforcement mechanisms.
In summary, the purpose of electoral bonds is to facilitate transparent funding of political parties while maintaining the anonymity of donors. However, concerns about the anonymity of donors, lack of disclosure, and potential misuse have led to criticism and scrutiny of the scheme.
What is the maximum amount of money that can be donated through electoral bonds.

The maximum amount of money that can be donated through electoral bonds is not explicitly stated in the provided search results. However, electoral bonds are available in various denominations, including ₹1,000, ₹10,000, ₹1,00,000, ₹10,00,000, and ₹1,00,00,000. The bonds are valid for 15 days after being issued, and political parties can receive electoral bonds issued by the public or corporations3. The bonds are available for purchase for ten days at the beginning of every quarter, and there are tax benefits for issuing electoral bonds. The donor must have a KYC compliant account to purchase the bonds and can donate to a political party or individual of their choice. The receiver collecting electoral bonds can encash the bonds through the party’s verified account.
Are there any restrictions on who can donate through electoral bonds
Based on the search results, there are no explicit restrictions on who can donate through electoral bonds. The bonds are available for purchase by any Indian corporate body, registered agency, or undivided Hindu family. The donor must have a KYC compliant account to purchase the bonds and can donate to a political party or individual of their choice. The bonds can be purchased digitally or with the help of a DD or cheque. However, the validity of electoral bonds is valid only for fifteen days, and they are available for purchase for ten days at the beginning of every quarter. The government may also specify an additional period of 30 days in the year of the Lok Sabha elections. The bonds are issued in multiples of ₹1,000, ₹10,000, ₹1,00,000, and ₹1,00,00,000, with a range between ₹1,000 and ₹1 crore.
What is the duration of validity of electoral bonds
Electoral bonds are financial instruments introduced by the Indian government to facilitate anonymous donations to political parties. They are available in denominations ranging from Rs. 1,000 to Rs. 1 crore and have a validity period of 15 days from the date of issuance. These bonds can only be purchased during specific 10-day periods in January, April, July, and October, as specified by the Central Government, with an additional 30-day window in a general election year.
The primary purpose of electoral bonds is to bring transparency to political funding by channeling donations through the banking system, reducing reliance on cash contributions. However, they have faced criticism for their anonymity, with concerns raised about the potential for misuse and lack of accountability.

Despite controversies, electoral bonds remain a significant aspect of political financing in India. Their availability in various denominations allows for contributions from a wide range of donors, contributing to the diversity of participation in the political process.
Overall, electoral bonds represent a unique approach to political funding, aiming to balance the need for transparency and accountability with the practicalities of financing political activities. However, ongoing debates and calls for reforms highlight the challenges in ensuring the integrity of the electoral process while accommodating the diverse interests of stakeholders involved in political financing.



